将数据映射到着色器
所有 SPIR-V 内容都是用 glslangValidator 生成的。
本章将介绍 Vulkan 中的 SPIR-V 与 shader 进行数据映射的方法,应用程序使用从 vkAllocateMemory 申请的 VkDeviceMemory 来映射数据,让 SPIR-V 着色器知道怎么使用这些数据。
在 Vulkan 核心功能中,主要有 5 种方法将数据从程序映射到 SPIR-V 中:
- 输入属性
- 描述符
- 描述符类型
- VK_DESCRIPTOR_TYPE_STORAGE_IMAGE
- VK_DESCRIPTOR_TYPE_SAMPLER 和 VK_DESCRIPTOR_TYPE_SAMPLED_IMAGE
- VK_DESCRIPTOR_TYPE_COMBINED_IMAGE_SAMPLER
- VK_DESCRIPTOR_TYPE_UNIFORM_BUFFER
- VK_DESCRIPTOR_TYPE_STORAGE_BUFFER
- VK_DESCRIPTOR_TYPE_UNIFORM_TEXEL_BUFFER
- VK_DESCRIPTOR_TYPE_STORAGE_TEXEL_BUFFER
- VK_DESCRIPTOR_TYPE_INPUT_ATTACHMENT
- 描述符类型
- 推送常量
- 特殊化常量
- 物理存储缓冲区
输入属性
Vulkan 中唯一具有输入属性的着色器阶段是顶点着色器 ( VK_SHADER_STAGE_VERTEX_BIT),需要在创建VkPipeline时显式声明,然后在绘制前将 VkBuffer 绑定到要映射的数据。其他着色器阶段(例如片段着色器)也有输入属性,但值是由在它之前运行的阶段输出的。
在调用vkCreateGraphicsPipelines之前 ,VkPipelineVertexInputStateCreateInfo 需要填入VkVertexInputAttributeDescription 数组,来映射输入属性到着色器。
GLSL 顶点着色器示例:
#version 450
layout(location = 0) in vec3 inPosition;
void main() {
gl_Position = vec4(inPosition, 1.0);
}
location 0 处只有一个输入属性,对应生成的 SPIR-V:
Name 18 "inPosition"
Decorate 18(inPosition) Location 0
17: TypePointer Input 16(fvec3)
18(inPosition): 17(ptr) Variable Input
19: 16(fvec3) Load 18(inPosition)
在这个例子中,VkVertexInputAttributeDescription的内容为:
VkVertexInputAttributeDescription input = {};
input.location = 0;
input.binding = 0;
input.format = VK_FORMAT_R32G32B32_SFLOAT; // maps to vec3
input.offset = 0;
下面要做的是在调用绘制前绑定顶点缓冲区和索引缓冲区(可选)。
“顶点缓冲区”需在创建 VkBuffer 时使用VK_BUFFER_USAGE_VERTEX_BUFFER_BIT 。
vkBeginCommandBuffer();
// ...
vkCmdBindVertexBuffer();
vkCmdDraw();
// ...
vkCmdBindVertexBuffer();
vkCmdBindIndexBuffer();
vkCmdDrawIndexed();
// ...
vkEndCommandBuffer();
更多信息请阅读顶点输入数据处理过程。
描述符
资源描述符 是将统一缓冲区(uniform buffer)、存储缓冲区(storage buffer)、采样器等数据映射到任何着色器阶段的主要方法。描述符一种的抽象理解是着色器可以使用的内存指针。
Vulkan 中有各种 描述符类型,Vulkan Spec有每种描述符类型的详细描述。
描述符被分组到 描述符 集合中,描述符集合绑定到着色器,即使描述符集中只有一个描述符,也要绑定整个VkDescriptorSet 到着色器。
举例
下例中有 3 个描述符集:
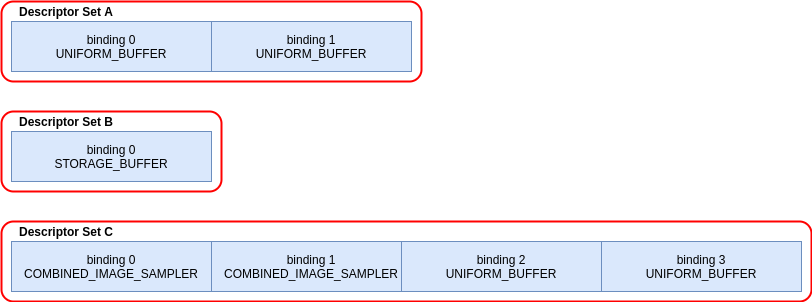
着色器的 GLSL:
// Note - only set 0 and 2 are used in this shader
layout(set = 0, binding = 0) uniform sampler2D myTextureSampler;
layout(set = 0, binding = 2) uniform uniformBuffer0 {
float someData;
} ubo_0;
layout(set = 0, binding = 3) uniform uniformBuffer1 {
float moreData;
} ubo_1;
layout(set = 2, binding = 0) buffer storageBuffer {
float myResults;
} ssbo;
相应的 SPIR-V:
Decorate 19(myTextureSampler) DescriptorSet 0
Decorate 19(myTextureSampler) Binding 0
MemberDecorate 29(uniformBuffer0) 0 Offset 0
Decorate 29(uniformBuffer0) Block
Decorate 31(ubo_0) DescriptorSet 0
Decorate 31(ubo_0) Binding 2
MemberDecorate 38(uniformBuffer1) 0 Offset 0
Decorate 38(uniformBuffer1) Block
Decorate 40(ubo_1) DescriptorSet 0
Decorate 40(ubo_1) Binding 3
MemberDecorate 44(storageBuffer) 0 Offset 0
Decorate 44(storageBuffer) BufferBlock
Decorate 46(ssbo) DescriptorSet 2
Decorate 46(ssbo) Binding 0
描述符的绑定是在记录命令缓冲区时完成的,描述符必须在调用draw/dispatch时绑定,以下伪代码:
vkBeginCommandBuffer();
// ...
vkCmdBindPipeline(); // Binds shader
// One possible way of binding the two sets
vkCmdBindDescriptorSets(firstSet = 0, pDescriptorSets = &descriptor_set_c);
vkCmdBindDescriptorSets(firstSet = 2, pDescriptorSets = &descriptor_set_b);
vkCmdDraw(); // or dispatch
// ...
vkEndCommandBuffer();
绑定结果如下:
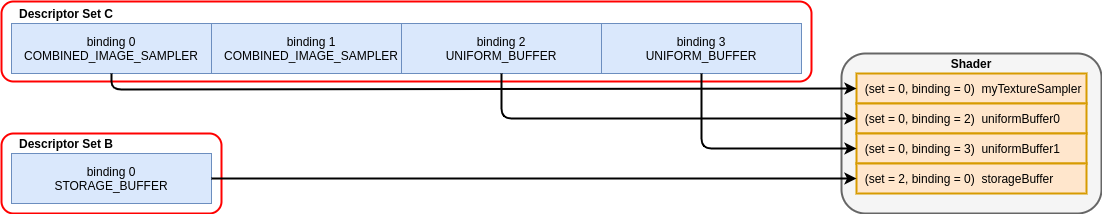
描述符类型
Vulkan Spec 有一个 着色器资源和存储对应类别 表,描述了每个描述符类型需要如何映射到 SPIR-V。
下面展示了 GLSL 和 SPIR-V 映射到每个描述符类型 的示例。
对于 GLSL,更多信息参阅: GLSL Spec - 12.2.4. Vulkan Only: Samplers, Images, Textures, and Buffers
存储图像(Storage Image)
VK_DESCRIPTOR_TYPE_STORAGE_IMAGE
// VK_FORMAT_R32_UINT
layout(set = 0, binding = 0, r32ui) uniform uimage2D storageImage;
// example usage for reading and writing in GLSL
const uvec4 texel = imageLoad(storageImage, ivec2(0, 0));
imageStore(storageImage, ivec2(1, 1), texel);
OpDecorate %storageImage DescriptorSet 0
OpDecorate %storageImage Binding 0
%r32ui = OpTypeImage %uint 2D 0 0 0 2 R32ui
%ptr = OpTypePointer UniformConstant %r32ui
%storageImage = OpVariable %ptr UniformConstant
采样器和采样图像(Sampler and Sampled Image)
VK_DESCRIPTOR_TYPE_SAMPLER`和`VK_DESCRIPTOR_TYPE_SAMPLED_IMAGE
layout(set = 0, binding = 0) uniform sampler samplerDescriptor;
layout(set = 0, binding = 1) uniform texture2D sampledImage;
// example usage of using texture() in GLSL
vec4 data = texture(sampler2D(sampledImage, samplerDescriptor), vec2(0.0, 0.0));
OpDecorate %sampledImage DescriptorSet 0
OpDecorate %sampledImage Binding 1
OpDecorate %samplerDescriptor DescriptorSet 0
OpDecorate %samplerDescriptor Binding 0
%image = OpTypeImage %float 2D 0 0 0 1 Unknown
%imagePtr = OpTypePointer UniformConstant %image
%sampledImage = OpVariable %imagePtr UniformConstant
%sampler = OpTypeSampler
%samplerPtr = OpTypePointer UniformConstant %sampler
%samplerDescriptor = OpVariable %samplerPtr UniformConstant
%imageLoad = OpLoad %image %sampledImage
%samplerLoad = OpLoad %sampler %samplerDescriptor
%sampleImageType = OpTypeSampledImage %image
%1 = OpSampledImage %sampleImageType %imageLoad %samplerLoad
%textureSampled = OpImageSampleExplicitLod %v4float %1 %coordinate Lod %float_0
组合图像采样器(Combined Image Sampler)
VK_DESCRIPTOR_TYPE_COMBINED_IMAGE_SAMPLER
在某些驱动实现中,使用组合图像采样器来进行图像采样 可能性能更高。
layout(set = 0, binding = 0) uniform sampler2D combinedImageSampler;
// example usage of using texture() in GLSL
vec4 data = texture(combinedImageSampler, vec2(0.0, 0.0));
OpDecorate %combinedImageSampler DescriptorSet 0
OpDecorate %combinedImageSampler Binding 0
%imageType = OpTypeImage %float 2D 0 0 0 1 Unknown
%sampleImageType = OpTypeSampledImage imageType
%ptr = OpTypePointer UniformConstant %sampleImageType
%combinedImageSampler = OpVariable %ptr UniformConstant
%load = OpLoad %sampleImageType %combinedImageSampler
%textureSampled = OpImageSampleExplicitLod %v4float %load %coordinate Lod %float_0
统一缓冲区(Uniform Buffer)
VK_DESCRIPTOR_TYPE_UNIFORM_BUFFER
统一缓冲区在绑�定时可以动态偏移(VK_DESCRIPTOR_TYPE_UNIFORM_BUFFER_DYNAMIC)
layout(set = 0, binding = 0) uniform uniformBuffer {
float a;
int b;
} ubo;
// example of reading from UBO in GLSL
int x = ubo.b + 1;
vec3 y = vec3(ubo.a);
OpMemberDecorate %uniformBuffer 0 Offset 0
OpMemberDecorate %uniformBuffer 1 Offset 4
OpDecorate %uniformBuffer Block
OpDecorate %ubo DescriptorSet 0
OpDecorate %ubo Binding 0
%uniformBuffer = OpTypeStruct %float %int
%ptr = OpTypePointer Uniform %uniformBuffer
%ubo = OpVariable %ptr Uniform
存储缓冲区(Storage Buffer)
VK_DESCRIPTOR_TYPE_STORAGE_BUFFER
存储缓冲区在绑定时可以动态偏移(VK_DESCRIPTOR_TYPE_STORAGE_BUFFER_DYNAMIC)
layout(set = 0, binding = 0) buffer storageBuffer {
float a;
int b;
} ssbo;
// example of reading and writing SSBO in GLSL
ssbo.a = ssbo.a + 1.0;
ssbo.b = ssbo.b + 1;
BufferBlock 和 Uniform 内容请阅读 VK_KHR_storage_buffer_storage_class
OpMemberDecorate %storageBuffer 0 Offset 0
OpMemberDecorate %storageBuffer 1 Offset 4
OpDecorate %storageBuffer Block
OpDecorate %ssbo DescriptorSet 0
OpDecorate %ssbo Binding 0
%storageBuffer = OpTypeStruct %float %int
%ptr = OpTypePointer StorageBuffer %storageBuffer
%ssbo = OpVariable %ptr StorageBuffer
统一纹素缓冲区(Uniform Texel Buffer)
VK_DESCRIPTOR_TYPE_UNIFORM_TEXEL_BUFFER
layout(set = 0, binding = 0) uniform textureBuffer uniformTexelBuffer;
// example of reading texel buffer in GLSL
vec4 data = texelFetch(uniformTexelBuffer, 0);
OpDecorate %uniformTexelBuffer DescriptorSet 0
OpDecorate %uniformTexelBuffer Binding 0
%texelBuffer = OpTypeImage %float Buffer 0 0 0 1 Unknown
%ptr = OpTypePointer UniformConstant %texelBuffer
%uniformTexelBuffer = OpVariable %ptr UniformConstant
存储纹素缓冲区(Storage Texel Buffer)
VK_DESCRIPTOR_TYPE_STORAGE_TEXEL_BUFFER
// VK_FORMAT_R8G8B8A8_UINT
layout(set = 0, binding = 0, rgba8ui) uniform uimageBuffer storageTexelBuffer;
// example of reading and writing texel buffer in GLSL
int offset = int(gl_GlobalInvocationID.x);
vec4 data = imageLoad(storageTexelBuffer, offset);
imageStore(storageTexelBuffer, offset, uvec4(0));
OpDecorate %storageTexelBuffer DescriptorSet 0
OpDecorate %storageTexelBuffer Binding 0
%rgba8ui = OpTypeImage %uint Buffer 0 0 0 2 Rgba8ui
%ptr = OpTypePointer UniformConstant %rgba8ui
%storageTexelBuffer = OpVariable %ptr UniformConstant
输入附件(Input Attachment)
VK_DESCRIPTOR_TYPE_INPUT_ATTACHMENT
layout (input_attachment_index = 0, set = 0, binding = 0) uniform subpassInput inputAttachment;
// example loading the attachment data in GLSL
vec4 data = subpassLoad(inputAttachment);
OpDecorate %inputAttachment DescriptorSet 0
OpDecorate %inputAttachment Binding 0
OpDecorate %inputAttachment InputAttachmentIndex 0
%subpass = OpTypeImage %float SubpassData 0 0 0 2 Unknown
%ptr = OpTypePointer UniformConstant %subpass
%inputAttachment = OpVariable %ptr UniformConstant
推送常量(Push Constants)
推送常量是在着色器中可访问的一组常量值,应用程序无需创建缓冲区或修改和绑定更新的描述符集,可以直接设置着色器中使用的值。
这种设计用于在命令缓冲区记录时高频更新少量(几个字节)数据的场景。
更多信息可以在 Push Constants 章节中找到。
特殊常量
特殊常量 是一种允许在创建VkPipeline时指定 SPIR-V 中的常量值的机制,这个功能非常强大,因为它取代了在高级着色语言(GLSL、HLSL 等)中执行预处理器宏的方法。
例子
如果应用程序想要创建的 VkPipeline 的每个shader的颜色值不同,一种简单的方法是使用两个着色器:
// shader_a.frag
#version 450
layout(location = 0) out vec4 outColor;
void main() {
outColor = vec4(0.0);
}
// shader_b.frag
#version 450
layout(location = 0) out vec4 outColor;
void main() {
outColor = vec4(1.0);
}
使用特殊常量,可以在调用vkCreateGraphicsPipelines编译着色器时做出选择 ,因此只需要一个着色器:
#version 450
layout (constant_id = 0) const float myColor = 1.0;
layout(location = 0) out vec4 outColor;
void main() {
outColor = vec4(myColor);
}
最终的 SPIR-V :
Decorate 9(outColor) Location 0
Decorate 10(myColor) SpecId 0
// 0x3f800000 as decimal which is 1.0 for a 32 bit float
10(myColor): 6(float) SpecConstant 1065353216
该值在着色器内仍是一个常量,但是如果另一个 VkPipeline 使用相同的着色器,想要将 myColor 设置为 0.5f,可以这样做:
struct myData {
float myColor = 1.0f;
} myData;
VkSpecializationMapEntry mapEntry = {};
mapEntry.constantID = 0; // matches constant_id in GLSL and SpecId in SPIR-V
mapEntry.offset = 0;
mapEntry.size = sizeof(float);
VkSpecializationInfo specializationInfo = {};
specializationInfo.mapEntryCount = 1;
specializationInfo.pMapEntries = &mapEntry;
specializationInfo.dataSize = sizeof(myData);
specializationInfo.pData = &myData;
VkGraphicsPipelineCreateInfo pipelineInfo = {};
pipelineInfo.pStages[fragIndex].pSpecializationInfo = &specializationInfo;
// Create first pipeline with myColor as 1.0
vkCreateGraphicsPipelines(&pipelineInfo);
// Create second pipeline with same shader, but sets different value
myData.myColor = 0.5f;
vkCreateGraphicsPipelines(&pipelineInfo);
第二个VkPipeline 的着色器解析myColor时将使用新常数值 0.5f�。
3 种特殊常量的用法
特殊常量通常有以下三种用法:
- 切换功能
- 直到运行时才知道 Vulkan 是否支持某项功能,嵌入一个运行时的常量决策从而避免编写两个单独的着色器。
- 改善后端优化
- 减小类型和内存大小
- 可以通过特殊常量设置使用的数组或变量类型的长度。
- 需要注意的是,编译器需要根据这些类型和大小来分配寄存器,如果分配的寄存器差异很大,管线缓存很可能会失败。
物理存储缓冲区
Vulkan 1.2 的VK_KHR_buffer_device_address 扩展添加了“着色器中的指针”功能。使用SPIR-V 中的 PhysicalStorageBuffer 存储类,应用程序可以调用 vkGetBufferDeviceAddress 返回内存的 VkDeviceAddress 。
这也是将数据映射到着色器的��一种方式。例如,如果应用程序想要将其与统一缓冲区一起使用,必须创建一个同时具有 VK_BUFFER_USAGE_SHADER_DEVICE_ADDRESS_BIT 和 VK_BUFFER_USAGE_UNIFORM_BUFFER_BIT的 VkBuffer,Vulkan 将使用描述符与着色器交互,随后可以使用物理存储缓冲区来更新值。
限制
以上的示例,还存在一些使用限制,限制一次可以绑定多少数据,这些限制如下:
- 输入属性
maxVertexInputAttributesmaxVertexInputAttributeOffset
- 描述符
maxBoundDescriptorSets- 每阶段限制
maxPerStageDescriptorSamplersmaxPerStageDescriptorUniformBuffersmaxPerStageDescriptorStorageBuffersmaxPerStageDescriptorSampledImagesmaxPerStageDescriptorStorageImagesmaxPerStageDescriptorInputAttachments- 每个类型限制
maxPerStageResourcesmaxDescriptorSetSamplersmaxDescriptorSetUniformBuffersmaxDescriptorSetUniformBuffersDynamicmaxDescriptorSetStorageBuffersmaxDescriptorSetStorageBuffersDynamicmaxDescriptorSetSampledImagesmaxDescriptorSetStorageImagesmaxDescriptorSetInputAttachmentsVkPhysicalDeviceDescriptorIndexingProperties(使用了 描述符索引)VkPhysicalDeviceInlineUniformBlockPropertiesEXT(使用了 Inline Uniform Block)
- 推送常量
maxPushConstantsSize128- 设备至少预留128字节